Introduction
Imagine your factory where machines are not just operated by humans, but can think like us humans, can make decisions, predict meltdowns, and also judge your employees for their inefficiency. 😄
Welcome to modern manufacturing, where AI isn’t a sci-fi advancement, but also the smartest employee your business can have.
From pinpointing your defects quicker than any human eye to organizing production better than your most experienced employee, AI is now reforming how factories functions, scale, and compete.
Your work, once required manual checks, endless spreadsheets, and crossed fingers, and now it’s handled by algorithms that learn, adapt, and optimize in real time.
In this blog, we’ll explore 8 powerful AI manufacturing use cases you absolutely shouldn’t miss. Not because they’re every other businesses are opting for it, but because they can save your firm’s costs, boosting productivity, and give you manufacturers a serious competitive edge.
What is AI Manufacturing?
This includes production, quality control, supply chain management, and predictive maintenance. This integration empowers manufacturers to automate repetitive tasks, optimise decision making, enhance product quality and streamline operations ultimately driving business growth.
AI tools can process and interpret vast amounts of data in production processes in real time, and more. This AI tools helps the manufacturers in gaining the end-to-end visibility of all manufacturing operations.
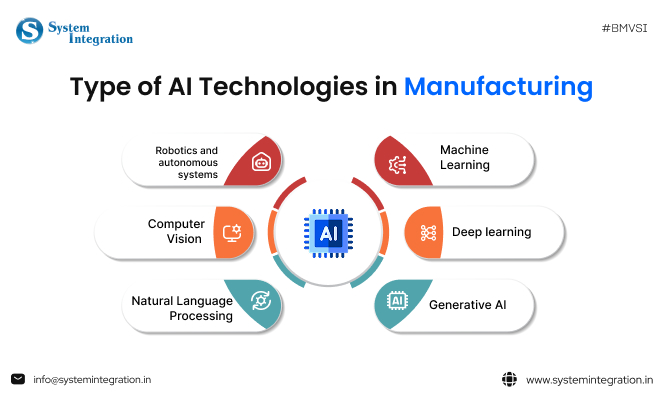
Key Benefits of AI in Manufacturing
➔ Increased efficiency and productivity: AI system can automate many routine and repetitive tasks.
➔ Improved quality control: the ability of AI to analyze the data in real time helps in improving the quality by identifying defects and anomalies in the production process.
➔ Predictive maintenance: AI can predict in advance that wether any machine is going to fail or its loosen elements and other errors. This helps in reducing the maintenance downtime.
➔ Better demand forecasting: AI can scan historical and current data within much less time and helps in forecasting the market trend and demand and help make more informed decisions.
➔ Cost saving: by automating tasks and enhancing the efficiency, AI can assist manufacturers lower labour costs.
➔ Enhanced safety: AI powered robots and machines can perform dangerous or hazardous tasks, reducing the risk of injury to human employee.
Real World 8 Use Cases of AI Manufacturing
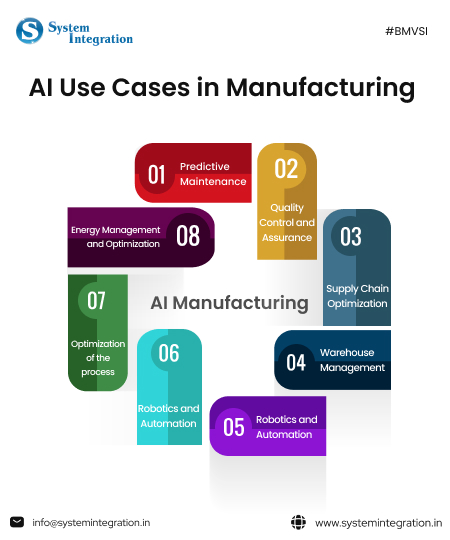
➢ Use Case 1: Automated Parts Sequencing
AI helps automotive parts suppliers overcome manual inefficiencies by implementing a real-time automation for parts sequencing that helps in enhancing accuracy, reducing errors, and enhancing traceability. It also reduce the inventory holding costs through “just in time” delivery, and enhanced product quality.
Benefits:
- AI adjusts sequencing in real-time, ensuring maximum, consistent accuracy.
- By precisely sequencing parts, manufacturers reduce the need for large and costly buffer stocks.
- AI can make real-time adoption to sudden changes in production, such as equipment failure or supply delay.
- The total plant efficiency increases with decreasing carbon footprint.
➢ Use Case 2: Predictive Maintenance
AI in manufacturing helps in reducing the downtime problem by predicting when the equipment is about to fail. With the help of AI incorporated software, it can analyze the historical data, read the sensors, and analyze the performance matrics. It can even forecast the maintenance needs in advance, allowing the business to perform repairs proactively.
Benefits:
- AI algorithms predict equipment failures before they occur, saving downtime.
- Lower maintenance, repair, and operational costs are achieved by reducing unnecessary repairs.
- By preventing the premature wear and tear and locating the issues early, equipment lasts longer, enhancing the ROI.
- AI optimizes maintenance planning, energy usage, and production efficiency, increasing their productivity upto 5-20%.
➢ Use Case 3: Quality Control and Assurance
AI enhances your business’s product quality by locating defects in real time operating the computer vision and machine learning models. AI also utilizes powered cameras and sensors to check products on production lines, recognize abnormalities, and ensure its alignment with quality norms quickly and more accurately than manual reviews.
Benefits:
- It’s consistent in maintaining your product quality, which improves “customer satisfaction” and “brand reputation”.
- AI can detect your product’s errors faster and inconsistencies with more precision, lowering human error.
- Real-time quality checks minimize your waste and save costs, and reduce rework.
- AI’s faster quality assurance cycles enhance your overall production value by up to 15–25%.
➢ Use Case 4: Supply Chain Optimization
AI enables your manufacturing business to optimize “supply chain operations” by forecasting demand, managing your inventory, and identifying disruptions. By analyzing your historical sales data, supplier performance, and “market trends”, AI ensures smooth material flow and timely production.
Benefits:
- Accurate in “demand forecasting” lowering overstocking and stockouts.
- AI driven insights improve your supplier selection and logistics planning.
- Lower inventory holding costs and improved cash flow are achieved.
- End-to-end supply chain visibility increases operational efficiency by 10–30%.
➢ Use Case 5: Warehouse Management
Storage, picking, packing, and inventory tracking are all optimised by AI-powered warehouse management systems. Using predictive analytics and automation, AI ensures efficient space utilisation and faster order fulfilment.
Benefits:
- AI lowers your manual tracking errors and increases inventory accuracy.
- Time and labour costs are decreased by optimised picking routes and warehouse layouts.
- Delivery schedules are improved by quicker order processing.
- AI Automation lowers operational bottlenecks and increases warehouse productivity.
➢ Use Case 6: Robotics and Automation
AI powered robots enable the automation of repetitive, unsafe, and accuracy-critical tasks on the factory floor. Smart robots are learning, adapting, and working with humans to increase efficiency on production lines and in the workplace.
Benefits:
- Robots with AI-accelerated capabilities enable your business with faster and more reliable productivity.
- On the workplace risk is limited by minimizing human involvement to dangerous operations.
- One of the biggest problem, downtime is minimised by error-free operation as well.
- Increasing demand is met with fast and reliable automation that scales.
➢ Use Case 7: Demand Forecasting
Artificial intelligence in manufacturing can use of information such as historical sales data, market trends, seasonal and customer buying behaviors to predict product demand more accurately. This allows manufacturers to better align production planning with the real market demand.
Benefits:
- AI helps forecasts become more accurate, which in turn decreases overproduction and shortages.
- Improved production planning will reduce inventory and storage charges.
- AI enables better alignment of production schedules with actual market needs.
- Better matching of demand triggers 10-25% greater overall operational efficiency.
➢ Case 8: Optimization of the process
Artificial Intelligence assesses production workflows to detect bottlenecks, inefficiencies and delays. Through continued learning from collected data, AI suggests process changes to help improve productivity.
Benefits:
- AI reveals invisible productivity leaks in production lines.
- Efficient automated workflows result in shorter cycle time and lower manufacturing costs.
- Marginal enhancements raise productivity from existing resources.
- Brands get more consistency and scalability.
Limitations of AI Manufacturing and How to Overcome Them
Bad Data Quality, and Silos of Data
Limitation:
AI systems are only as intelligent as the data they learn from. In manufacturing, information is frequently siloed in ERP, MES, SCADA and legacy systems. False assumptions and inaccurate behaviors come from incomplete, contradictory or outdated information.
Solution:
- Set up a centralized data architecture
- Clean and label old production data in real time.
- Leverage IoT Sensors to Collect Reliable Data from Machines
- Enforce data governance principles to maintain quality over time
High Implementation and Integration Costs
Limitation:
Adoption of AI in manufacturing involves substantial upfront investment: new hardware, sensors, AI platforms and system integrations. For small and mid-sized manufacturers, that cost can be a hurdle.
Solution:
- Begin with high ROI tasks(e.g., predictive maintenance, quality inspection)
- Leverage cloud AI platforms to minimize infrastructure needs
- Utilize no-code/low-code automation tools such as n8n for quick integrations
- Adopt AI incrementally versus broad scale rollouts
Integration with Existing Systems
Limitation:
But manufacturing plants frequently use machines and software that are decades old, developed at a time when AI was virtually nonexistent, making integration into the production line complex and time consuming.
Solution:
- Leverage APIs, middleware and automation platforms to connect legacy and modern systems
- Utilize edge AI solutions to interlink old machines without full overhauling
- Fix systems and processes in small modifications, rather than the wholesale re-design.
- Leveraging AI tools compliant with industrial standards safe for interoperable adoption
Trust, Transparency, and Explainability Issues
Limitation:
AI models can act as “black boxes” in ways that makes it difficult for operators and decision makers to trust automatic recommendations, especially where public safety is concerned.
Solution:
- Adopting AI: use AI models that explain why actions are taken
- Superchange processes with AI insights and human validation
- Regularly check and audit AI models for bias or accuracy
- Ensure accountability between human teams and AI systems is well-defined
Wrapping up Thoughts
From pinpointing your defects quicker than any human eye to organizing production better than your most experienced employee, AI is now reforming how manufacturing industries functions, scale, and compete.
After exploring 8 powerful AI in manufacturing use cases they can save your firm’s costs, boosting productivity, and give you manufacturers a serious competitive edge.
Although, tackling with unstructured data for better output can be tough for the business. However, this can be solved by partnering with the best AI software development company, as they have a team of experienced developers who can boost your manufacturing efficiency.
FAQs
AI uses machine learning, computer vision, and predictive analytics to help manufacturers automate their daily tasks, predict the future forecast and more.
It reduces the downtime
Lower the labor costs
Prevents machine breakdowns
Improves quality control
Enhances decision making
Firstly, decide the tasks you want to automate and start by automating the small tasks as you are new to this. Than decide the best fitting AI tools for those tasks and integrate them into your existing software or create your own custom software.
Generative AI in manufacturing utilizes AI algorithms to generate new and innovative solutions for manufacturing processes. Generative AI can be used for tasks like product design, process optimization and doubt about material selection.